Dexcom technology is more accessible than ever before
In England and Wales, NICE (The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence)* has guidelines on funding CGM for some people with diabetes.
- Adults and children with type 1 diabetes should be offered a choice of glucose sensor.1,2 Read the full NICE guidance here
- For people with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes, a glucose sensor can be considered, based on certain criteria.3 Read the full NICE guidance here
NICE recommends hybrid closed loop systems (CGM with a connected insulin pump†) as an option for managing glucose, for all people with type 1 diabetes meeting any of the following criteria:*,4
- Age 18 or under with type 1 diabetes
- Over 18 with HbA1c greater than 7.5%
- Those that suffer from disabling hypoglycaemia
- People who are pregnant or trying to conceive
In Scotland, SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guideline Network) has guidelines on access to people with type 1 diabetes that covers.5
- Eligibility for CGM and hybrid closed loop systems
- Factors to support the choice of CGM
- Offering CGM to all children and young people with type 1 diabetes, alongside education and support for their families and carers
Your Diabetes Healthcare Team will have their own local policy which they use in line with the NICE and SIGN guidelines. Speak to them at your next visit and ask what the guidelines mean for you.

Know what you need
Speaking with your Diabetes Healthcare Team is important to ensure you get the right CGM. There are some things you should consider before your appointment, such as deciding what your goals and needs are.
To help you confidently prepare for your discussion, we have created a handy checklist to fill out and take with you.
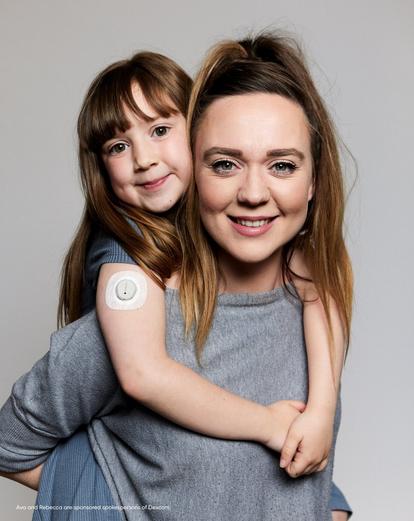

'As a parent of a child with Type 1, you have to learn to be flexible. There were so many times, especially when she was first diagnosed, when it felt like our lives had to fit around Ava’s disease…not the other way around. When we got on Dexcom CGM System, it was like the weight was lifted. We finally have a tool to help us get more control.'
Rebecca,
Mum to Dexcom Warrior Ava
Mum to Dexcom Warrior Ava

The Dexcom difference
With Dexcom CGM technology, you receive automatic glucose readings straight to your compatible smartphone or optional receiver.§
Customisable alerts and alarms help keep you in range6 throughout the day – without finger pricks¶ or scanning.
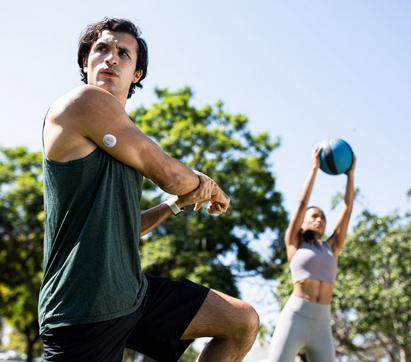
Know your numbers
Dexcom real-time CGM devices help you to understand how food, exercise, stress, and more can affect your glucose levels. So you can confidently make more informed decisions about your diabetes.
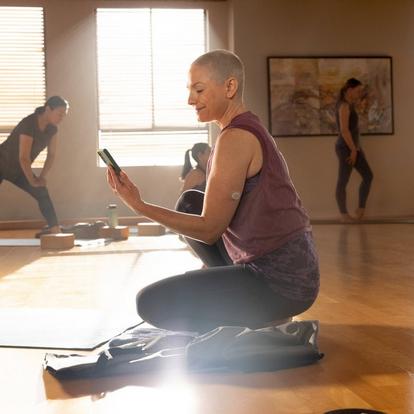

In sync with your glucose levels –whenever, wherever
Dexcom CGM devices are proven to lower HbA1c, increase time in range7-13 and improve overall wellbeing.8,9,13 All with no scanning, ever.
With multiple wear locations,|| customisable alerts and alert schedules, you can personalise your Dexcom CGM system to suit your lifestyle.
Whatever your diabetes needs are, we have a CGM for you
Which Dexcom CGM device would best suit your needs? The best way to find the right device for you is to talk to your Diabetes Healthcare Team who can discuss what your goals are.
§ Smart devices sold separately.

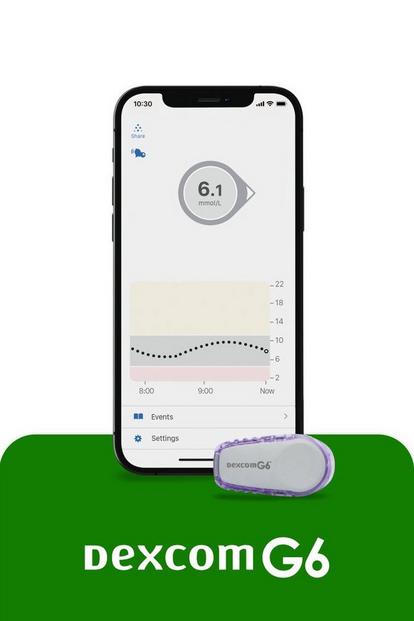
CGM made more accessible
Best for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who are looking for an easy CGM that's available on prescription.
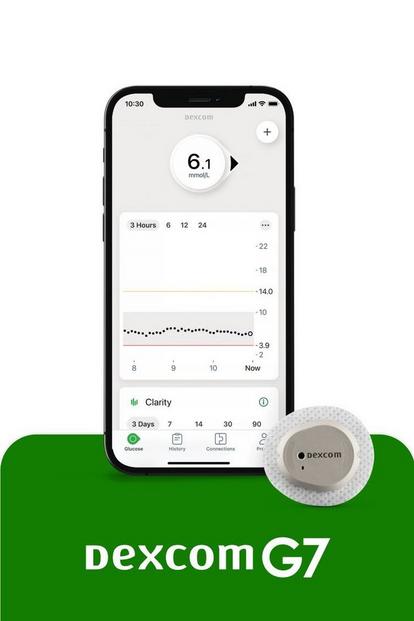
Powerful and connected CGM
Best for people with type 1 diabetes who may need extra support, such as people who are hypo unaware, pregnant or children, and those that want connectivity with insulin delivery systems and health or lifestyle apps.
Powerful and connected CGM
Best for people with type 1 diabetes who may need extra support, such as people who are hypo unaware, pregnant or children, and those that want connectivity with insulin delivery systems and health or lifestyle apps.
Help understanding diabetes
Diabetes can be overwhelming. Dexcom is proud to partner with prominent diabetes charities such as JDRF and Diabetes UK, who both have a wealth of knowledge and advice on their websites to help you understand your condition.

A charity dedicated to helping people with type 1 diabetes, the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation fund world-class medical research to cure, prevent and treat type 1 diabetes.

Diabetes UK is a British-based patient, healthcare professional and research charity that campaigns for improvements in the care and treatment of people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
*© NICE [2024]. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights. NICE guidance is prepared for the National Health Service in England. All NICE guidance is subject to regular review and may be updated or withdrawn. NICE accepts no responsibility for the use of its content in this product/publication.
† Compatible insulin-delivery devices sold separately. For a list of compatible devices, please visit www.dexcom.com/compatibility.
‡ Ava and Rebecca are sponsored spokespersons of Dexcom.
§ Display devices sold separately. For a list of compatible smart devices, please visit www.dexcom.com/compatibility.
¶ If your glucose alerts and readings from a Dexcom CGM System do not match symptoms or expectations, use a blood glucose meter to make diabetes treatment decisions.
|| Dexcom G6 can be worn on the back of the upper arm, abdomen and upper buttocks for children ages 2-17. Dexcom G7 and Dexcom ONE+ can be worn on the back of the upper arm, abdomen and upper buttocks for children ages 2-6.
1 Type 1 diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline [NG17]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng17.
2 Diabetes (type 1 and type 2) in children and young people: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline [NG18]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng18.
3 Type 2 diabetes in adults: management. NICE guideline [NG28]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng28.
4 Hybrid closed loop systems for managing blood glucose levels in type 1 diabetes [TA10845]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/indevelopment/gid-ta10845.
5 Optimising glycaemic control in people living with type 1 diabetes (toolkit) - https://www.sign.ac.uk/our-guidelines/optimising-glycaemic-control-in-people-with-type-1-diabetes/.
6 Acciaroli G, et al. Mitigation of Rebound Hyperglycemia With Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data and Predictive Alert. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2022;16(3):677-682.
7 Aleppo G, et al. The Effect of Discontinuing Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Treated With Basal Insulin. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(12):2729-2737.
8 Lind M, et al. Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes Treated With Multiple Daily Insulin Injections: The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017;317(4):379-387.
9 Lind M, et al. Sustained Intensive Treatment and Long-term Effects on HbA1c Reduction (SILVER Study) by CGM in People With Type 1 GOLD RCT Diabetes Treated With MDI. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(1):141-149.
10 Welsh JB, et al. Comparisons of Fifth-, Sixth-, and Seventh-Generation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024;18(1):143-147.
11 Beck RW, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring versus usual care in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving multiple daily insulin injections: A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(6):365-374.
12 Beck RW, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: The DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317(4):371-378
13 Visser MM, et al. Effect of switching from intermittently scanned to real-time continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes: 24-month results from the randomised ALERTT1 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023;11:96–108.
† Compatible insulin-delivery devices sold separately. For a list of compatible devices, please visit www.dexcom.com/compatibility.
‡ Ava and Rebecca are sponsored spokespersons of Dexcom.
§ Display devices sold separately. For a list of compatible smart devices, please visit www.dexcom.com/compatibility.
¶ If your glucose alerts and readings from a Dexcom CGM System do not match symptoms or expectations, use a blood glucose meter to make diabetes treatment decisions.
|| Dexcom G6 can be worn on the back of the upper arm, abdomen and upper buttocks for children ages 2-17. Dexcom G7 and Dexcom ONE+ can be worn on the back of the upper arm, abdomen and upper buttocks for children ages 2-6.
1 Type 1 diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline [NG17]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng17.
2 Diabetes (type 1 and type 2) in children and young people: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline [NG18]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng18.
3 Type 2 diabetes in adults: management. NICE guideline [NG28]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng28.
4 Hybrid closed loop systems for managing blood glucose levels in type 1 diabetes [TA10845]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/indevelopment/gid-ta10845.
5 Optimising glycaemic control in people living with type 1 diabetes (toolkit) - https://www.sign.ac.uk/our-guidelines/optimising-glycaemic-control-in-people-with-type-1-diabetes/.
6 Acciaroli G, et al. Mitigation of Rebound Hyperglycemia With Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data and Predictive Alert. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2022;16(3):677-682.
7 Aleppo G, et al. The Effect of Discontinuing Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Treated With Basal Insulin. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(12):2729-2737.
8 Lind M, et al. Continuous Glucose Monitoring vs Conventional Therapy for Glycemic Control in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes Treated With Multiple Daily Insulin Injections: The GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017;317(4):379-387.
9 Lind M, et al. Sustained Intensive Treatment and Long-term Effects on HbA1c Reduction (SILVER Study) by CGM in People With Type 1 GOLD RCT Diabetes Treated With MDI. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(1):141-149.
10 Welsh JB, et al. Comparisons of Fifth-, Sixth-, and Seventh-Generation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024;18(1):143-147.
11 Beck RW, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring versus usual care in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving multiple daily insulin injections: A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(6):365-374.
12 Beck RW, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: The DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317(4):371-378
13 Visser MM, et al. Effect of switching from intermittently scanned to real-time continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes: 24-month results from the randomised ALERTT1 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023;11:96–108.
